Chapitre 15
Activité 3 - Activité expérimentale
L'étoile Polaire
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Problématique de l'activité
Depuis des millénaires, les explorateurs de l'hémisphère nord ont scruté le ciel à la recherche de l'étoile Polaire pour se repérer. Également appelée l'étoile du Nord, elle a pour particularité de se situer presque sur la direction de l'axe de rotation de la Terre et de rester fixe dans le ciel céleste
Comment déterminer le type spectral d'une étoile ?
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
À l'œil nu, les étoiles semblent n'être que des points semblables, indifférenciables les unes des autres. Est-ce vraiment le cas ?
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 1 Types spectraux d'étoiles
| Type | \lambda_{\max } (en nm) | Raies d'absorption |
| O | \lt 110 | \mathrm{H}, \mathrm{He}, \mathrm{He}^{+} |
| B | 110 - 290 | \mathrm{H}, \mathrm{He} |
| A | 290 - 390 | \mathrm{H}, \mathrm{Ca}^{+} |
| F | 390 - 480 | \mathrm{H}, \mathrm{Fe}, \mathrm{Fe}^{+}, \mathrm{Ti}, \mathrm{Ti}^{+}, \mathrm{Ca}^{+}, \mathrm{Na}, \mathrm{Mg} |
| G | 480 - 580 | \mathrm{Fe}, \mathrm{Fe}^{+}, \mathrm{Ti}, \mathrm{Ti}^{+}, \mathrm{Ca}^{+}, \mathrm{Na}, \mathrm{CH} |
| K | 580 - 830 | \mathrm{Fe}, \mathrm{Ti}, \mathrm{CH} |
| M | > 830 | \mathrm{Fe}, \mathrm{Ti}, \mathrm{CH}, \mathrm{TiO} |
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 2 Données de l'étoile Polaire
Les données correspondant à l'intensité I des radiations émises par l'étoile Polaire pour des longueurs d'onde comprises entre 200 et 2 000 nm sont à retrouver en ligne. Ces données sont brutes. Elles peuvent néanmoins être importées dans un tableur pour y être exploitées.
Retrouvez les données de l'étoile Polaire .
Retrouvez les données de l'étoile Polaire .
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
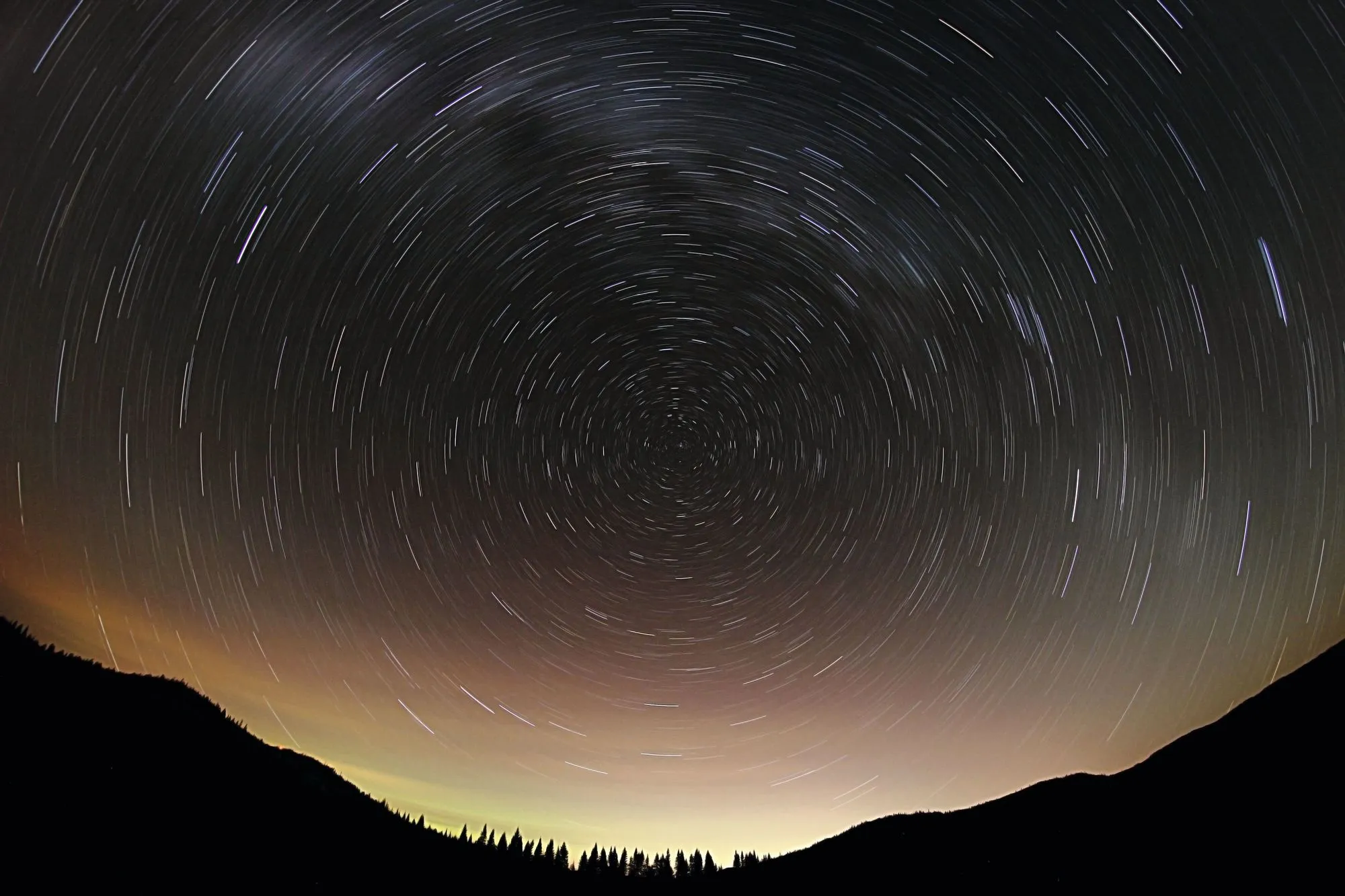
Doc. 3 Photographie nocturne en pause longue


Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
| Longueurs d'onde, en nanomètres, de raies caractéristiques pour diverses entités chimiques | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| \mathrm{H} | 434,0 486,1 656,3 | \mathrm{He} | 447,1 587,6 | \mathrm{Ti} | 453,5 501,4 | \mathrm{Mg} | 517,3 719,3 | \mathrm{Fe} | 527,0 778,3 |
| \mathrm{Ca}^{+} | 645,7 | \mathrm{Na} | 589,6 | \mathrm{CH} | 430,0 | \mathrm{TiO} | 761,2 | \mathrm{Fe}^{+} | 625,0 |
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Questions
Compétence(s)
APP : Extraire l'information utile sur des supports variés
MATH : Utiliser des outils numériques
MATH : Utiliser des outils numériques
1. Doc. 2 Tracer l'évolution de l'intensité lumineuse relative émise par l'étoile Polaire, notée I, en fonction de la longueur d'onde \lambda à partir des données numériques.
2. Mesurer \lambda_{\max } à partir de la représentation graphique obtenue.
3. Identifier la présence ou l'absence des raies d'absorption caractéristiques d'entités chimiques à partir des données.
4. Doc. 1 En déduire le type spectral de l'étoile Polaire.
3. Identifier la présence ou l'absence des raies d'absorption caractéristiques d'entités chimiques à partir des données.
4. Doc. 1 En déduire le type spectral de l'étoile Polaire.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Synthèse de l'activité
Quels sont les paramètres permettant de déterminer le type spectral d'une étoile ?
Une erreur sur la page ? Une idée à proposer ?
Nos manuels sont collaboratifs, n'hésitez pas à nous en faire part.
j'ai une idée !
Oups, une coquille