Chapitre 8
Cours
Structure des entités organiques
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
1La structure des molécules
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
AQu'est‑ce qu'une molécule organique ?
Autrefois, les molécules organiques étaient issues du règne animal ou végétal, ce n'est plus forcément le cas aujourd'hui. Les molécules organiques d'origine naturelle ou de synthèse sont définies par rapport à leur composition.
On considère qu'une molécule est organique si elle comporte des atomes de carbone et d'hydrogène liés entre eux et éventuellement d'autres atomes (\text{O}, \text{N}, \text{Cl}, etc.).
On considère qu'une molécule est organique si elle comporte des atomes de carbone et d'hydrogène liés entre eux et éventuellement d'autres atomes (\text{O}, \text{N}, \text{Cl}, etc.).
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 1Les molécules organiques

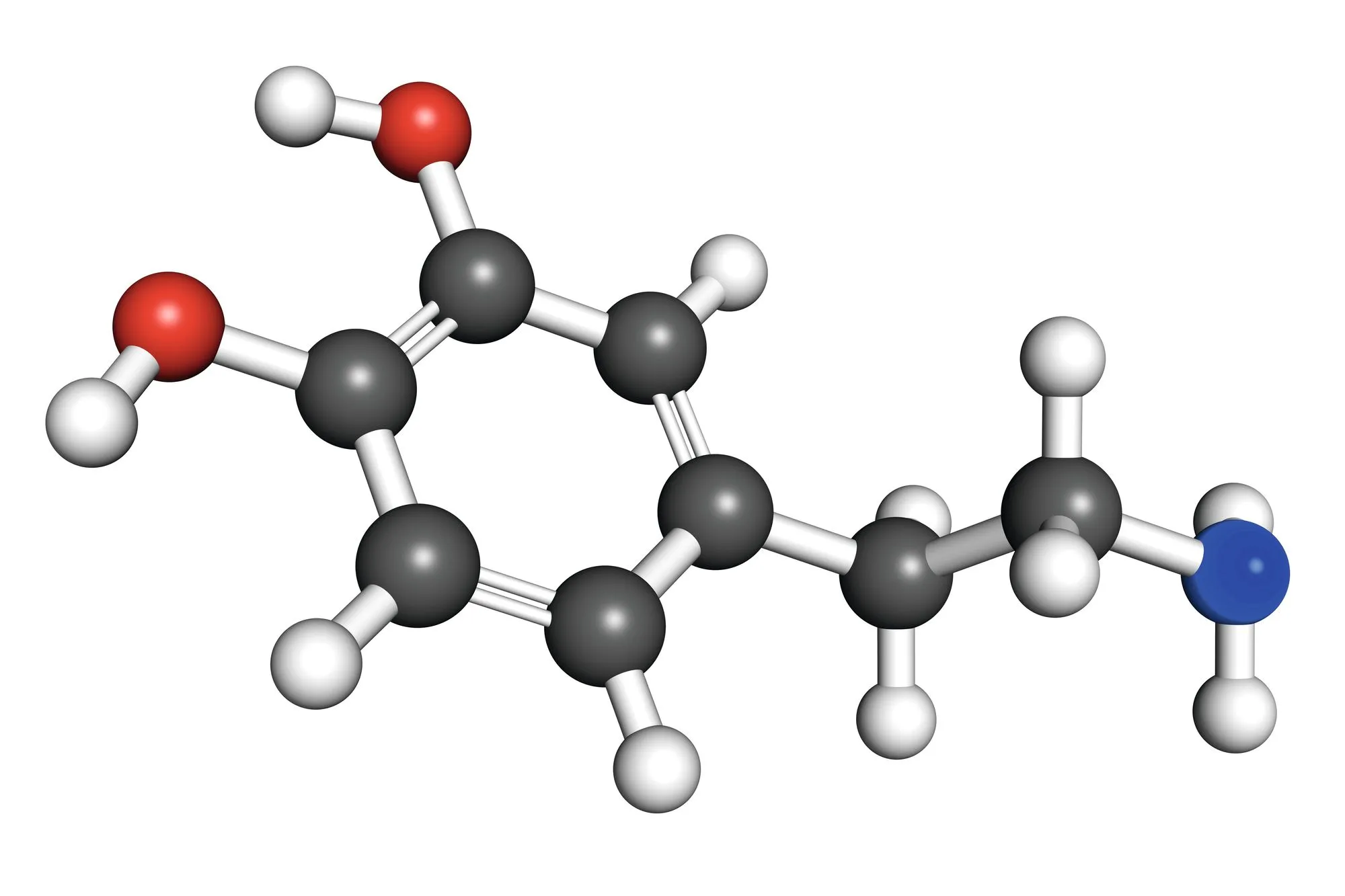
Dopamine : molécule organique qui constitue l'hormone du plaisir. Les molécules organiques ont pour base un squelette d'atomes de carbone et d'hydrogène mais elles peuvent être composées de nombreux autres atomes.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
BFormules brutes et semi‑développées
Une molécule est formée par un assemblage d'atomes. Elle est électriquement neutre.
Pour respecter les règles de l'octet et du duet, les atomes vont créer des liaisons covalentes et former des molécules pour gagner en stabilité. Il existe plusieurs manières de représenter une molécule, certaines permettant de visualiser ces liaisons internes.
Exemple : la représentation d'une molécule d'éthanol.

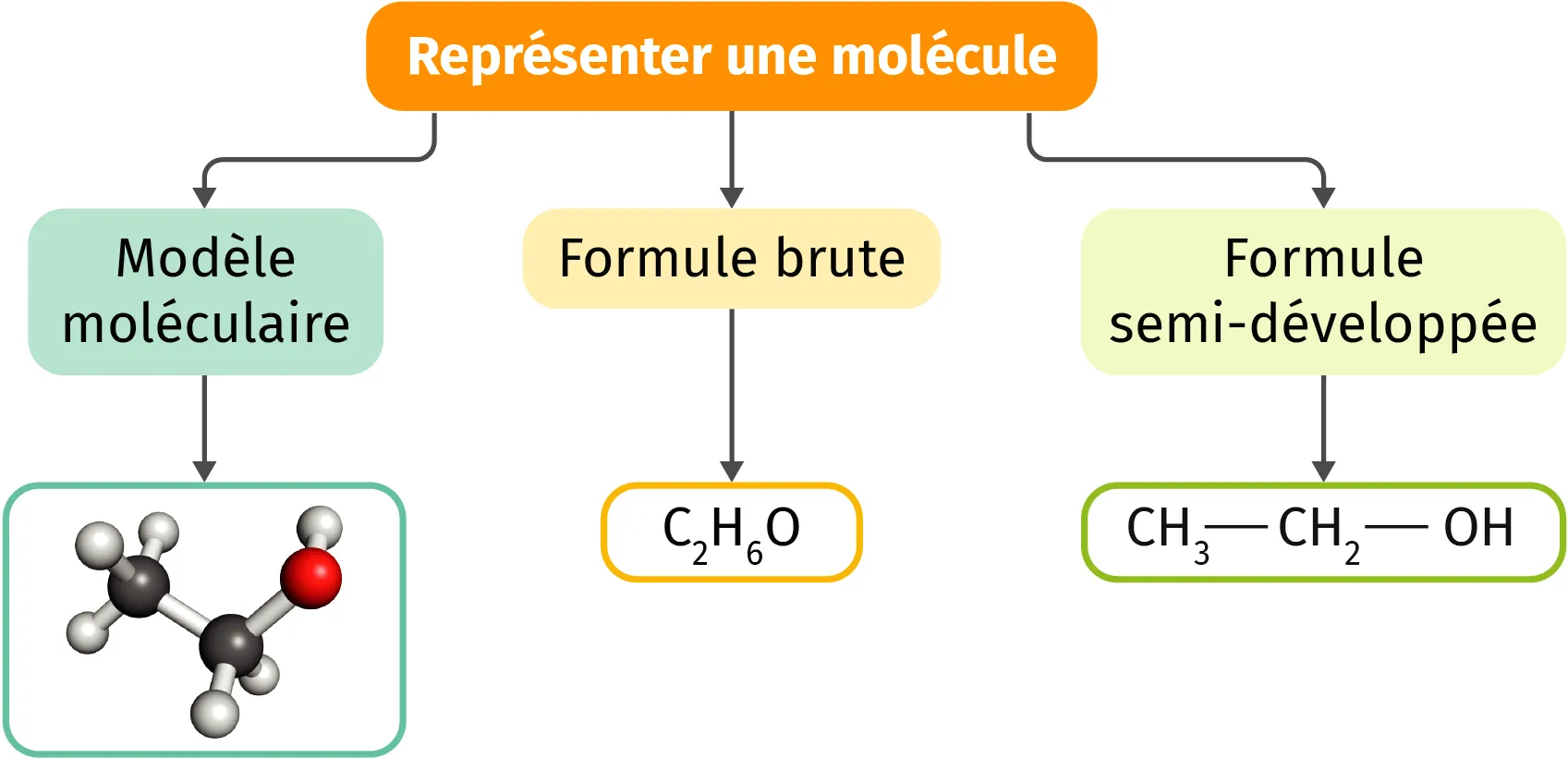
Pour respecter les règles de l'octet et du duet, les atomes vont créer des liaisons covalentes et former des molécules pour gagner en stabilité. Il existe plusieurs manières de représenter une molécule, certaines permettant de visualiser ces liaisons internes.
Exemple : la représentation d'une molécule d'éthanol.


Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
En formant une liaison, un atome gagne un électron. Le nombre de liaisons formées est déterminé grâce aux règles du duet ou de l'octet.
|
Atome |
C |
H |
O |
|
Nombre de liaisons |
4 |
1 | 2 |
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
CGroupes caractéristiques
Un groupe caractéristique est un groupement d'atomes autres que les atomes de carbone et d'hydrogène qui confère des propriétés chimiques particulières aux molécules. Les molécules qui ont le même groupe caractéristique font partie de la même famille chimique.
Voici les principaux groupes caractéristiques à connaître :
|
Famille |
Alcool |
Aldéhyde |
Cétone |
Acide carboxylique |
|
Nom du groupe |
Hydroxyle |
Carbonyle |
Carboxyle | |
|
Représentation du groupe |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 2 Molécule polyfonctionnelle

La molécule d'acide citrique, présente dans le citron, possède plusieurs groupes caractéristiques.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Attention, un groupe carboxyle n'est pas un groupe carbonyle + un groupe hydroxyle !
L'aldéhyde et la cétone ont tous les deux un groupe carbonyle mais ce sont deux familles différentes :
L'aldéhyde et la cétone ont tous les deux un groupe carbonyle mais ce sont deux familles différentes :
- les aldéhydes ont un groupe carbonyle en fin de chaîne carbonée ;
- les cétones ont un groupe carbonyle dans la chaîne carbonée.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
2Nommer des molécules
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
ANommer une chaîne carbonée
Une molécule organique possède un enchaînement d'atome de carbone qui constitue son squelette appelé chaîne carbonée.
Une chaîne carbonée possédant uniquement des liaisons \text{C} - \text{C} et \text{C} - \text{H} est appelée alcane.
Une chaîne carbonée est dite linéaire si les atomes de carbone s'enchaînent en se formant les uns à la suite des autres.
Une chaîne est dite ramifiée si au moins un des atomes de carbone de la chaîne linéaire est relié à plus de deux atomes de carbone. Les groupes qui forment la ramifi cation sont appelés groupes alkyles.
Dans le cas d'un alcane ramifié, il faut repérer la chaîne carbonée principale qui est la chaîne carbonée la plus longue. On numérote ensuite cette chaîne carbonée et on rajoute le nom des ramifications (groupes alkyles).
On numérote la chaîne carbonée de manière à ce que les groupes caractéristiques puis les ramifications alkyles portent le plus petit numéro (doc. 4). On nomme les groupes alkyles par ordre alphabétique et on les précède de leur numéro de position.
Exemple : voici une molécule à deux ramifications.
Une chaîne carbonée possédant uniquement des liaisons \text{C} - \text{C} et \text{C} - \text{H} est appelée alcane.
Une chaîne carbonée est dite linéaire si les atomes de carbone s'enchaînent en se formant les uns à la suite des autres.
Une chaîne est dite ramifiée si au moins un des atomes de carbone de la chaîne linéaire est relié à plus de deux atomes de carbone. Les groupes qui forment la ramifi cation sont appelés groupes alkyles.
Dans le cas d'un alcane ramifié, il faut repérer la chaîne carbonée principale qui est la chaîne carbonée la plus longue. On numérote ensuite cette chaîne carbonée et on rajoute le nom des ramifications (groupes alkyles).
On numérote la chaîne carbonée de manière à ce que les groupes caractéristiques puis les ramifications alkyles portent le plus petit numéro (doc. 4). On nomme les groupes alkyles par ordre alphabétique et on les précède de leur numéro de position.
Exemple : voici une molécule à deux ramifications.

Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 3 Préfixes des alcanes et alkyles
|
Nombre d’atomes de carbone |
Préfixe |
|
1 |
Méth- |
|
2 |
Éth- |
|
3 | Prop- |
|
4 | But- |
|
5 |
Pent- |
|
6 |
Hex- |
|
7 | Hept- |
|
8 | Oct- |
|
9 | Non- |
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Attention, la chaîne carbonée principale est celle qui comporte le plus grand nombre d'atomes de carbone, elle n'est pas toujours représentée en ligne droite.


Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 4 Groupes alkyles identiques

Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
BNommer une molécule avec un groupe caractéristique
Les suffixes des groupes caractéristiques principaux sont données ci-dessous.
|
Famille |
Alcool |
Aldéhyde |
Cétone |
Acide carboxylique |
|
Terminaison |
n-ol |
n-al |
n-one |
Acide-oïque |
Avec n le numéro de l'atome de carbone sur lequel est fixé le groupe caractéristique.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 5 Détail du nom d'une molécule

Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
3Comment identifier une molécule ?
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
ALa spectroscopie IR : une technique d'analyse
La spectroscopie infrarouge, appelée spectroscopie IR, est une technique d'analyse des molécules en chimie organique. Cette technique étudie l'absorption de la lumière infrarouge par les molécules. L'absorption de cette lumière est liée à la vibration des liaisons dans les
molécules suite à une excitation électromagnétique.
Chaque type de liaison vibre à une fréquence particulière et cette fréquence est reliée au nombre d'onde noté \sigma (en cm-1). Les nombres d'onde v étudiés correspondent à des longueurs d'onde \lambda ( \sigma = \dfrac{1}{\lambda} ) du domaine des infrarouges (750 nm \lt \lambda \lt 0,1 mm).
Un spectre IR représente la transmittance T (en %) en fonction du nombre d'onde \sigma (en cm-1).
Chaque type de liaison vibre à une fréquence particulière et cette fréquence est reliée au nombre d'onde noté \sigma (en cm-1). Les nombres d'onde v étudiés correspondent à des longueurs d'onde \lambda ( \sigma = \dfrac{1}{\lambda} ) du domaine des infrarouges (750 nm \lt \lambda \lt 0,1 mm).
Un spectre IR représente la transmittance T (en %) en fonction du nombre d'onde \sigma (en cm-1).
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 6 Les liaisons \text{O - H} pour un alcool
Deux molécules d'alcool peuvent établir des liaisons hydrogène () entre elles. On distingue alors deux types de liaisons \text{O} - \text{H} :
- \text{O} - \text{H} libre : à l'état gazeux, quand les molécules sont trop éloignées pour former des liaisons hydrogène,
→ la bande dans le spectre IR est alors fine ; - \text{O} - \text{H} lié : à l'état liquide, les molécules sont rapprochées et peuvent donc faire des liaisons hydrogène,
→ la bande dans le spectre IR est alors large et son nombre d'onde est plus faible comparé à une liaison \text{O} - \text{H} libre.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
BIdentification d'une molécule
On peut identifier les différents types de liaisons présentes dans une molécule grâce à la spectroscopie infrarouge (IR).
La présence d'une liaison dans la molécule se manifeste par la présence d'une bande d'absorption caractéristique, que l'on reconnaît par son allure et son nombre d'onde.
Chaque liaison dans la molécule va vibrer dans une plage de nombres d'onde référencée dans les tables. Le doc. 7 en présente un court extrait.
La présence d'une liaison dans la molécule se manifeste par la présence d'une bande d'absorption caractéristique, que l'on reconnaît par son allure et son nombre d'onde.
Chaque liaison dans la molécule va vibrer dans une plage de nombres d'onde référencée dans les tables. Le doc. 7 en présente un court extrait.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Doc. 7 Bandes d'absorption IR
|
Liaison |
\sigma (cm ‑1) |
Forme |
|
\text{O} - \text{H} libre |
3 580 - 3 650 |
Bande fine |
|
\text{O} - \text{H} lié |
3 200 - 3 400 |
Bande large |
|
\text{C} - \text{H} alcane |
2 800 - 3 100 |
Plusieurs bandes |
|
\text{O} - \text{H} acide carboxylique |
2 500 - 3 200 | Bande large |
|
\text{C} = \text{O} aldéhyde et cétone |
1 650 - 1 730 | - |
|
\text{C} = \text{O} acide carboxylique |
1 680 - 1 710 | - |
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Application

Corrigé
Sur le spectre IR de la molécule inconnue, on remarque une bande caractéristique de la liaison \text{O} - \text{H} d'un acide carboxylique aux alentours de 3 000 cm-1.
De plus, elle présente une bande aux alentours de 1 700 cm-1 caractéristique de liaison \text{C} = \text{O} d'un acide carboxylique.
Cette molécule comporte les deux bandes caractéristiques d'un acide carboxylique, c'est donc un acide carboxylique.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Retrouvez une sur la lecture des spectres IR en cliquant ici.
Une erreur sur la page ? Une idée à proposer ?
Nos manuels sont collaboratifs, n'hésitez pas à nous en faire part.
j'ai une idée !
Oups, une coquille